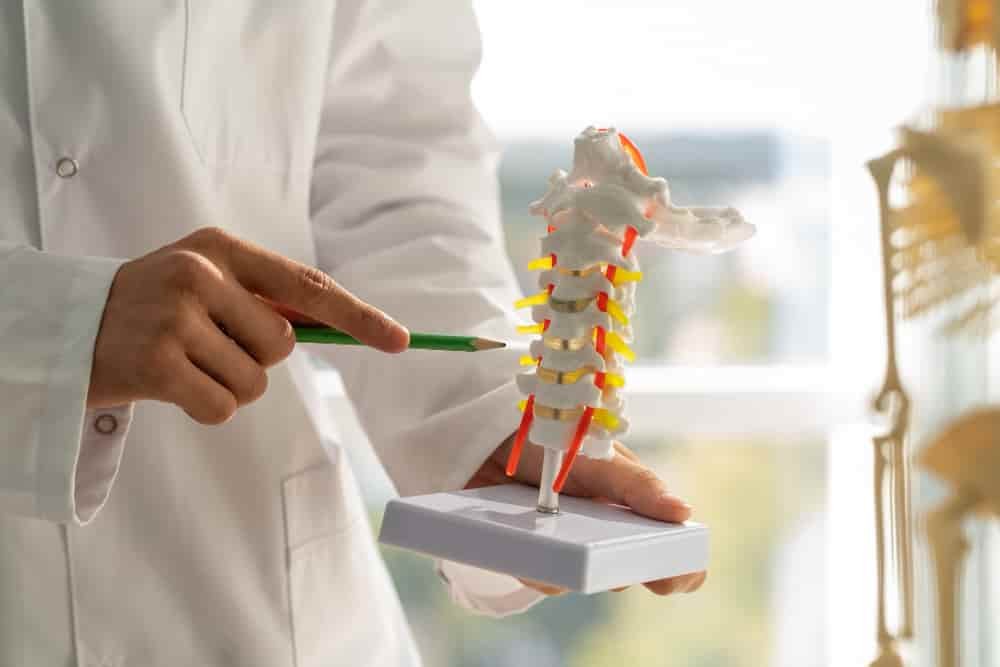
Spine problems can cause significant discomfort and affect daily life. From slipped discs to spinal tumors, understanding common conditions is crucial for early detection and appropriate treatment. In this article, we explore various spine issues, their causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
Your spine is protected by a cushion-like disc called a vertebra. As you age, these disks become dried out and can tear or break under the pressure of too much stress. This condition is often referred to as herniated disk, and it may not be immediately noticeable. In some cases, symptoms like pain in your arms or legs might occur, and if this isn’t treated with exercise and medication, surgery may be necessary.
Cervical spondylosis is a degenerative disease that affects the thickness and density of discs in your neck. These disks serve as cushioning between your vertebrae, and can become compressed due to cervical spondylosis. This condition becomes more common with age. However, many people who suffer from it and don’t experience any symptoms until later in life.
Spinal cord injuries happen when there is damage to the spinal cord. This can be caused by accidents, such as a fall or car crash, or by something like cancer that has spread to the spine. In most cases, this results in bruising the spinal cord or part of its blood supply being cut off. That can cause serious problems for your brain because it prevents it from controlling parts of your body properly.
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most commonly occurring form of arthritis. It affects millions of people worldwide, primarily affecting joints in the hands, knees, hips, and spine. It occurs when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones wears down over time. Maintaining a healthy weight and engaging in regular physical activity can help slow down the disease process and improve joint function.
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a condition that results from the narrowing of one or more bony openings within the spine. This can be caused by age-related changes, as well as injuries sustained during your lifetime. Symptoms include back or neck pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the arms and legs.
Tumor
Spinal tumors are masses of tissue that can occur within or around the spinal cord and/or spine, commonly due to primary cancers. Common metastatic sites for these diseases include lung, breast, and prostate.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition that can cause your spine to twist sideways. The most common type of scoliosis affects children during their growth spurt, before puberty. This will often result in one shoulder blade being higher than the other.
Kyphosis
This condition causes your spine to curve forward. It is most common in older women, but it can also affect children if their spines develop incorrectly. This can cause pain and other problems, and in severe cases, the curvature of your spine may bend your whole body out of shape. Treatment might include medication or physical therapy to help you recover.
Cervical spondylolisthesis is a condition in which the vertebrae on one side of the spine move to an abnormal position relative to those above and below them. This can occur as we age, but it also occurs during periods of intense stress or activity, like playing football, gymnastics, and weightlifting. Rest and lifestyle changes should help. If the pain keeps up, you may need proper treatment or even surgery.
If you experience any of the following symptoms, be sure to call your spine doctor right away: feeling weak or numb in your arms and legs, experiencing pain that does not come from physical activity and is more severe at night, or worsening over time.
The treatment options for spine problems depend on the specific condition and its severity. Non-surgical approaches often include medication, physical therapy, and exercise to alleviate pain, improve mobility, and strengthen the supporting muscles. In some cases, spinal injections, such as epidural steroid injections, can provide temporary relief. However, if conservative measures fail to provide sufficient improvement, surgery may be considered.