Lumbar Decompression Treatment
This is one of the commonest procedures performed on the Lumbar spine. There are many causes for pressure on the nerves in the lumbar region. These include
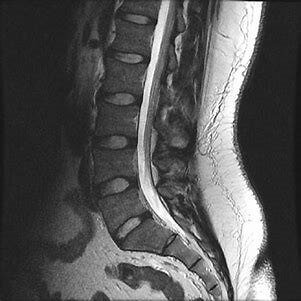
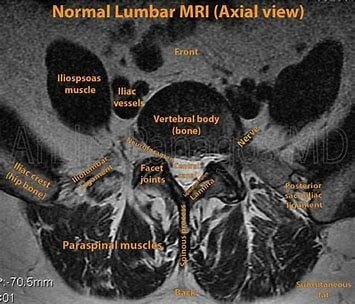
- Disc buldge or herniation
- Synovial Cyst, ie. the cyst coming out from the facetal joints
- Or a combination of facetal arthropathy, with ligamental hypertrophy, bony spurs and disc herniation.

- All this results into the narrowing of the spinal canal resulting into symptoms like backache, radiculopathy (Sciatica), tingling and numbness in the legs and even weakness of the lower limbs, if the compression is severe.
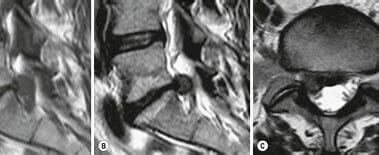
- Extruded Disc
The initial treatment, in most cases is conservative. Surgery is needed as an emergency only if the patient comes with acute weakness of limbs with loss of bladder and bowel control.
Initial bed rest, observation and anti-inflammatory drugs is the first line of treatment. Most of the patients recover with this treatment. Only in few patients, who have intractable pain and the symptoms are not relieved for 4-6 weeks may undergo radiological imaging like X-Ray and MRI.
Around 70-80% of the patients respond well to conservative management. In some patients where there is mild to moderate neural compression injecting steroids around the nerves could be beneficial. Patients with severe compression without instability, lumbar decompression is a good option.
Lumbar decompression can be performed as an
- Open procedure
- Minimally invasive procedure
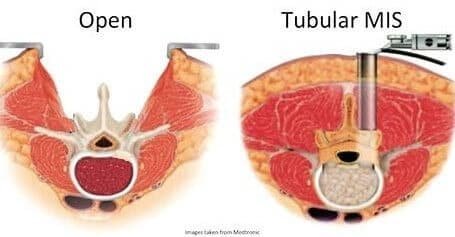
Open Procedure: In open procedure, the skin is incised and muscle are separated and retracted. The bony window is made and decompression is done. It involves more wear and tear of muscles, more blood loss and more post-operative pain.

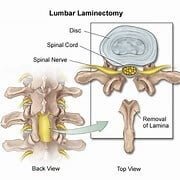
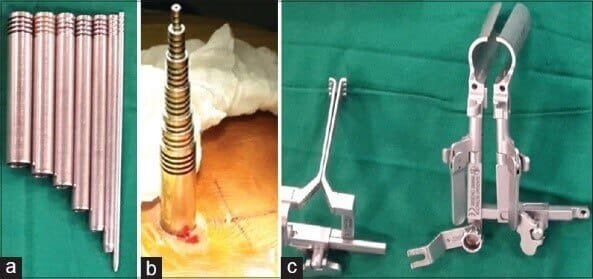
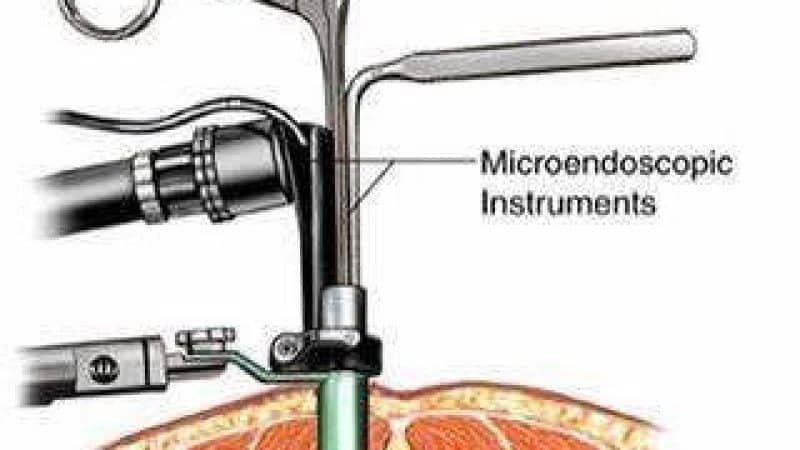
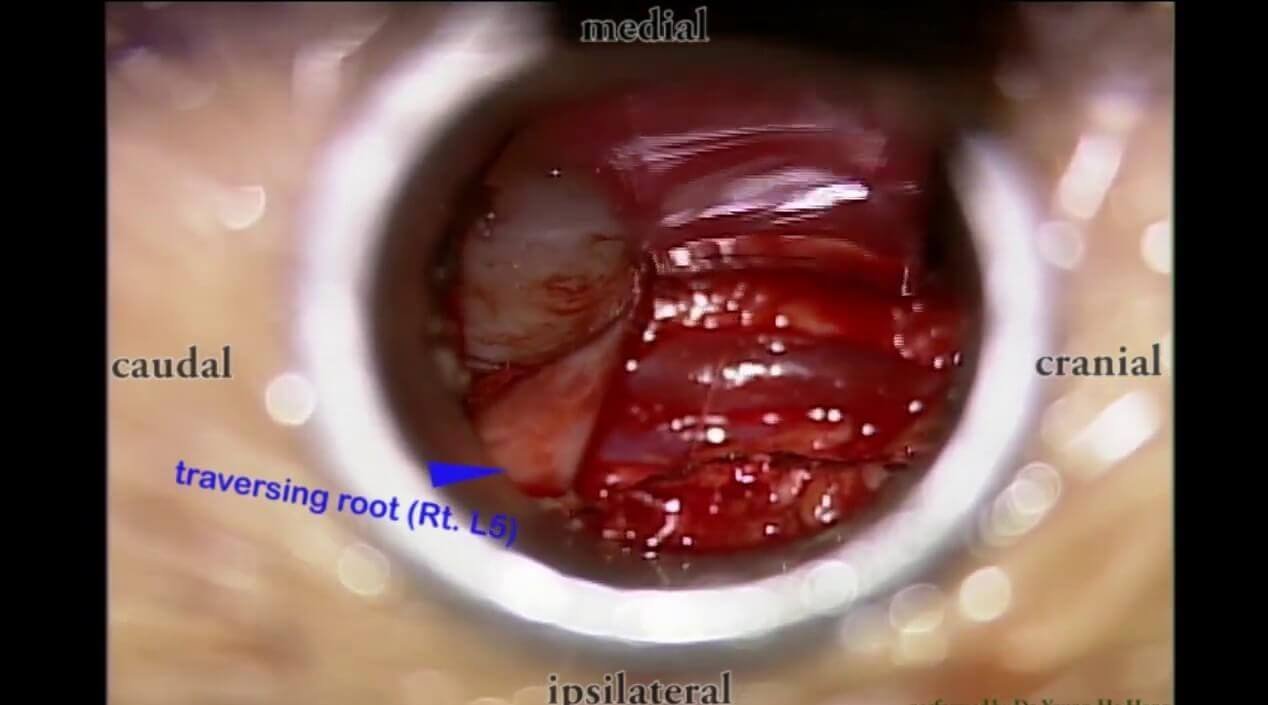
Minimally Invasive Procedure: In this the tubular retractor system is used, and serially the muscle fibers are spread using dilators to reach the bone. Later, the bone is removed through the tubular retractor i.e. laminotomy or laminectomy. Then the offending cause like the bony spur (osteophyte), herniated disc, synovial cyst, facetal hypertrophy causing compression on the nerve root is removed using specialized tools under a microscope or an endoscope. It involves less wear and tear of muscles, less blood loss, small incision (2cm) and less post-operative pain.