Pituitary Tumor Surgery
Pituitary Tumor Surgery in Pune
These are tumors of the pituitary gland. It accounts for around 10-15% of the adult brain tumors. Majority of them are adenomas are less than 5 mm in diameter and require no treatment. Only serial observation along with radiology is required.
The pituitary gland sits at the base of the skull in the Sella turcica which is a part of the sphenoidal bone.
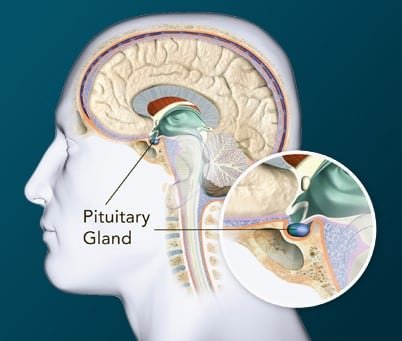
The main function of the pituitary gland is to secrete hormone. Whenever there is an adenoma, we divide it many ways.
Sometimes, according to the size of the tumor.
- Tumor less than 1 cm is called a microadenoma
- Tumor more than 1 cm is macroadenoma.
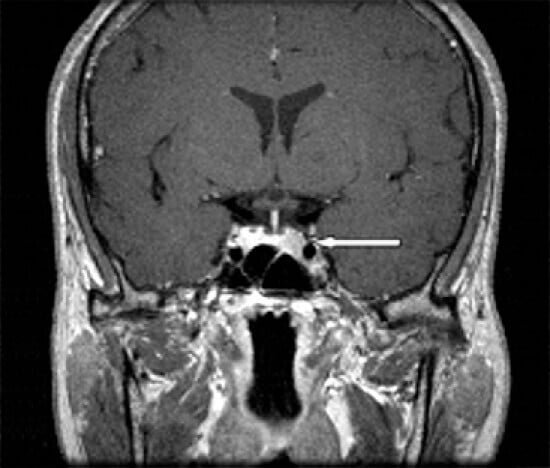
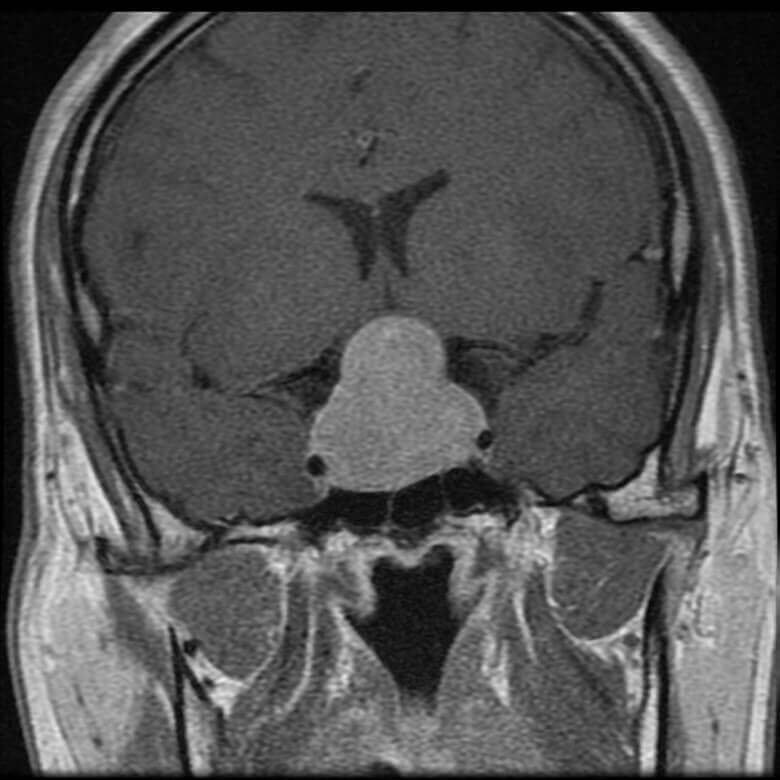
Sometime, according to the type of hormone secreted
- Non secretory adenomas: these tumors do not secrete any hormones and are usually silent in the initial phase. Then with time they increase in size and grow big. When they grow more than 1 cm in size, they are known as non-secretory pituitary macro adenomas. These tumors are manifested late and are quite big at the time of diagnosis, when they start compressing the surrounding structures mainly the visual pathway causing visual field changes. In these patients’ surgery is required to decompress the optic pathway and the gland.
- Secretory adenomas: these tumors are hormone secreting tumors and are usually manifested early because the excess hormone produce some changes in the body and cause symptoms.
- Among these 40-60% patient secrete hormone called “prolactin” which causes lactation, decreased libido and infertility in both males and females.
- About 30% patient secrete “growth Hormone”. In kids this excess secretion will cause gigantism while in adults it can cause increase in hand size and coarsening of facial features.
- Among 15-20% the tumor starts secreting ACTH “corticotropin” and causes symptoms like obesity, diabetes, high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
Then in such patients the symptoms need to be addressed. There are few medications that can reverse the symptoms and decrease the hormone secretion of prolactin, called cabergoline, bromocriptine and pergolide. This medication actually shrinks the size of the tumor and the need for surgery can be abandoned. However, excess growth hormone or corticotropin secreting tumors can be dangerous, so these tumors are mostly treated by surgery.
Initial Work up:
- Laboratory investigations– To check all the pituitary hormonal level.
- Ophthalmic evaluation: Vision evaluation, with visual field, and fundus examination.
- MRI Brain: We need to do a special type of MRI called the dynamic MRI with sellar cuts.
It is always advisable for the patient to see an endocrinologist and a neurosurgeon to decide the management.
Surgery:
Most the pituitary adenoma can be removed through minimally invasive endoscopic transnasal trans-sphenoidal surgery. In this, there is actually no external incision. We enter through the nose with the help of the endoscopic camera and get access to the area of interest. After surgery, patient is discharged on the 5th day after the removal of the nasal pack.
Sometime, when the tumor is very big with a large suprasellar and parasellar component; in such cases a two-stage surgery is required. In the 1st stage we do an endoscopic nasal approach and remove the tumor as much as possible, 2nd stage we need to do a craniotomy to remove the residual tumor.
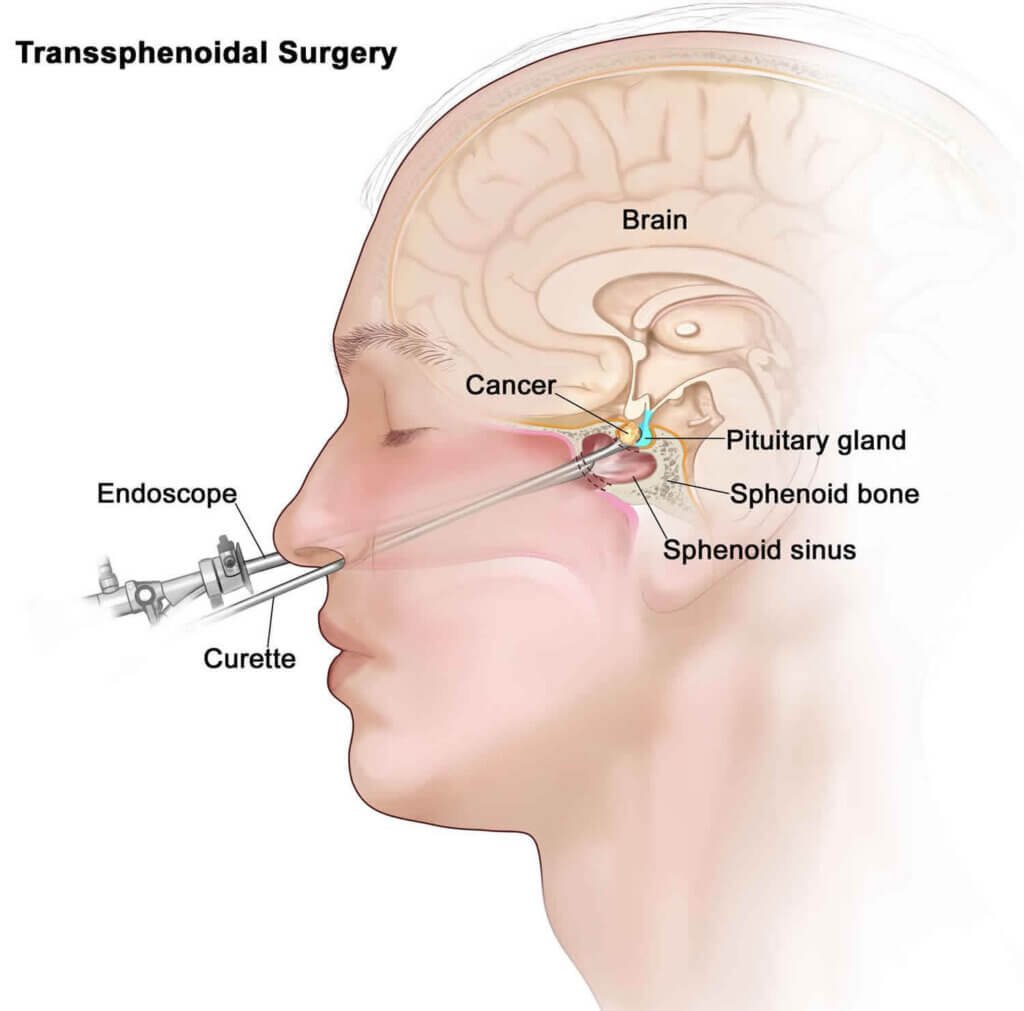
Radiation:
It is given in few tumors that recur following surgery or a very small component of the tumor is left behind.