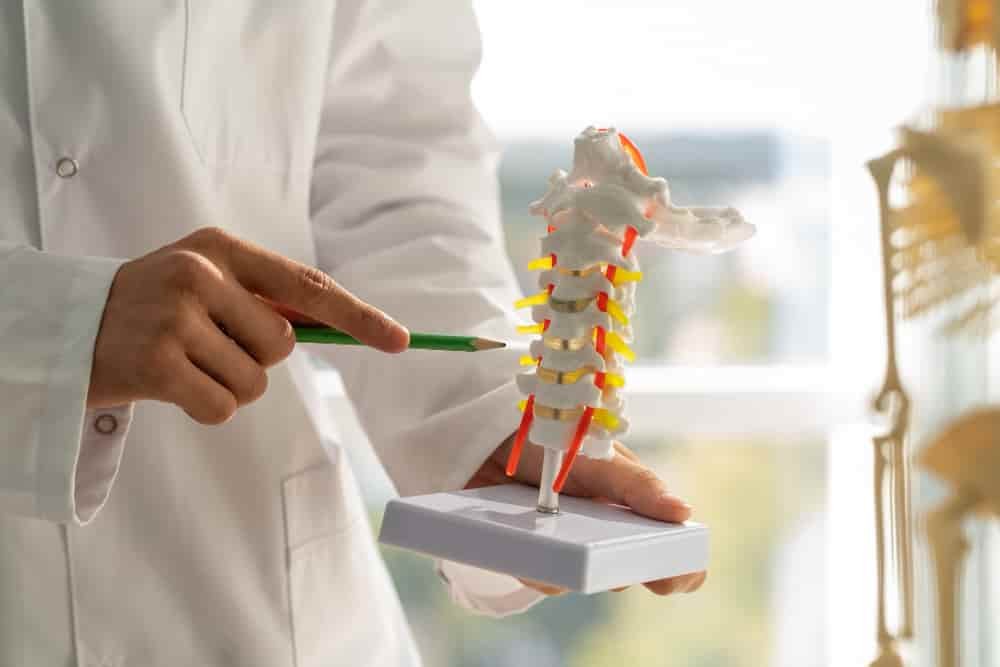
What is an intervertebral disc prolapse?
An intervertebral disc is a cushion between the two vertebral bodies which acts as a shock absorber and gives flexibility to the vertebral column. It mainly consists of an outer fibrous structure called the annulus fibrosus and an inner gelatinous structure called nucleus pulposus. Any tear to the annular structure results in leaking of this gelatinous structure to the outside and is known as herniated disc.
Who gets a herniated disc?
Sitting for a long time in the same position, being overweight, lifting heavy objects, frequent turning or twisting for work, sports or recreation, smoking. People ages 30-50 are most likely to get a herniated disc.
What causes a herniated disc?
The discs consist of an outer fibrous structure called the annulus fibrosus and an inner gelatinous structure called nucleus pulposus, like a jelly donut. Over time, the outer structure due to wear and tear, weakens and can crack. A bulging disc occurs when the “jelly” inside material leaks out of the fissure. A leak can press on nearby nerves. A single excessive strain or injury may cause a herniated disc.
What factors contribute to disc herniation?
- Aging
- Overweight
- Repetitive motion
- Accidental
- Impact from improper lifting or turning
- Sedentary Lifestyle
Symptoms of Herniated Disc?
Most herniated discs occur in the lower back, but they can also occur in the neck. Signs and symptoms depend on the location of the disc and how much pressure it is putting on the exiting or traversing nerve root.
Pain: If a herniated disc is in your lower back, in addition to lower back pain, you will often have pain radiating to the hips, thighs, buttocks and calf. For a herniated disc in the neck, you will often have pain in your shoulders, arms and forearm. It all depends on the nerve root involved and whether the compression is unilateral or bilateral. This pain can get aggravated by coughing, straining, yawning or changing to certain positions. The pain is often described as sharp or burning.
Numbness or tingling: People with a herniated disc often experience pain or tingling in the part of the body where the affected nerve works. He may also have altered sensation with paraesthesia.
Muscle weakness: Sometimes they may also present as weakness in the muscles to which the involved nerve root supply. It can cause you to stumble or impair your ability to lift or hold things.
When should you see a doctor?
Initially, you can treat herniated disc pain at home by taking some rest or analgesics. But you should see a spine specialist if
- Pain interferes with daily life
- Symptoms do not improve after four to six weeks or even worsen or even aggravate
- Develop a loss of bowel or bowel control
- Trouble in standing or walking.
- Saddle anaesthesia: Loss of sensation around the anal canal, medial thigh and
What is the evaluation process?
Your neurosurgeon will first do a physical examination. Then they can take x-rays. Some people may require an MRI if the herniated disc symptoms are not getting improved or even worsening.
What is the treatment for a herniated disc?
Eighty to ninety percent herniated disc patients can be treated just by conservative treatment which includes rest, medication and physiotherapy. If you have lower back pain, your spine doctor may recommend physical therapy. This exercise can help you strengthen the abdominal muscles and other muscles that support the spine.
Medication: Some analgesics can be very useful.
Physiotherapy: A physiotherapist teaches you exercise techniques to help you reduce stress on your muscles. Exercise strengthens the muscles and improves circulation.
Spinal Injections: Also called an epidural nerve block. A spinal injection is an injection of steroids directly into the area surrounding the involved nerve root. The medicine reduces the swelling and inflammation and ease symptoms. This will allow your body to recover and get back to work faster.
For non-emergency conditions, spine surgery is an option when other treatments fail. There are different ways to perform herniated disc surgery, but the goal is to reduce the compression over the nerve root.
A Note by Dr. Vishal Bhasme (Spine Specialist in Pune)
Having a herniated disc can cause you to feel unsteady. But don’t panic– the slightest movement can make the pain worse when you stand up because of the muscular spasm. Try to be active and follow your doctor’s recommendations for stretching. Gentle movement combined with pain killers helps most people feel better within a few weeks.